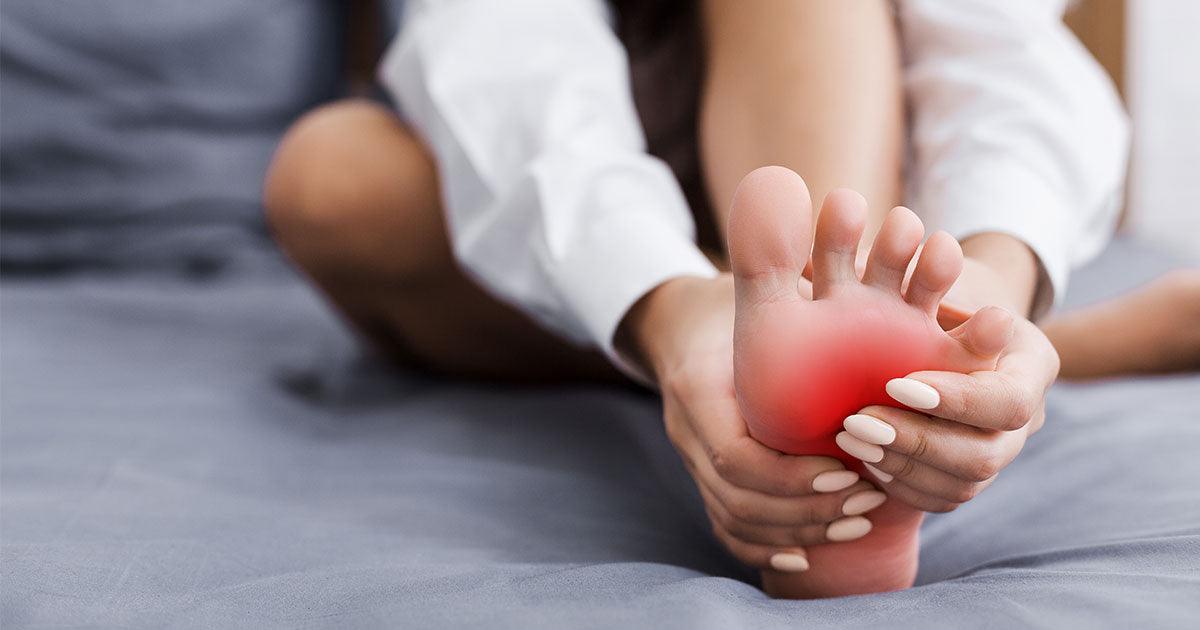
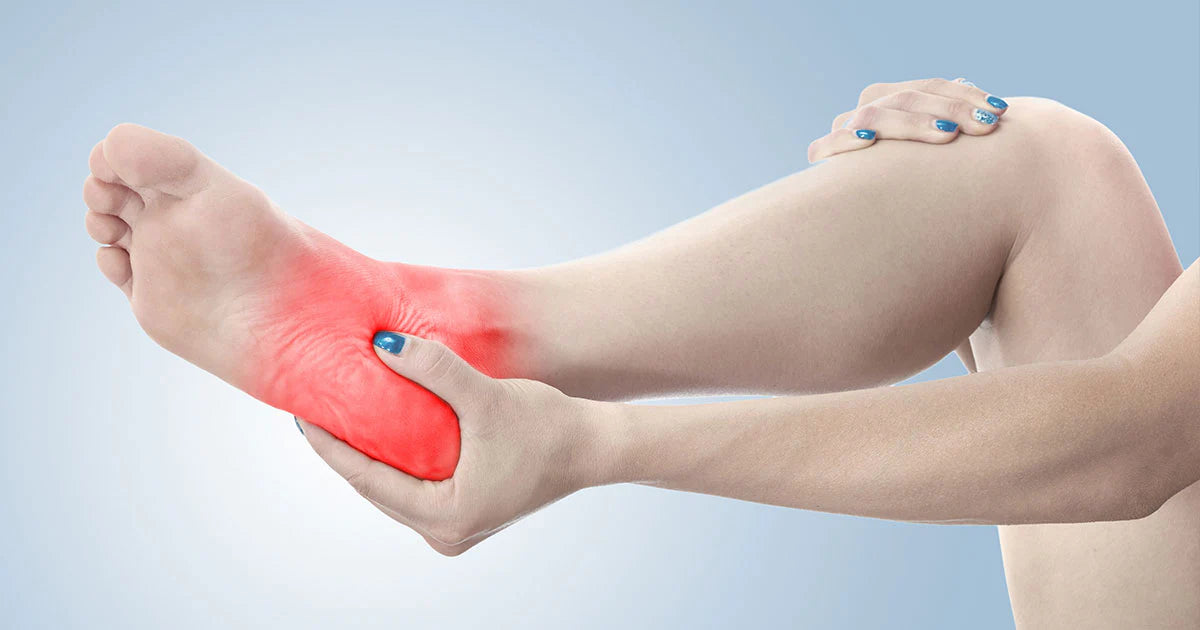
Many people suffering from Achilles Tendonitis symptoms experience swelling and mild to severe pain in the ankle area. Achilles tendonitis symptoms typically begin as a mild ache in the back of the leg or above the heel after running or other sports activity. Your pain may come on gradually, or you may only experience it when you walk or run.
Achilles Tendonitis Symptoms
You may find that you have less strength and range of movement in the ankle than usual if you have Achilles tendonitis symptoms. Some people find that walking with Achilles tendonitis becomes extremely difficult. Episodes of more severe tendon pain may occur after prolonged running, stair climbing or sprinting. You might also experience tenderness or stiffness, particularly in the morning, which usually improves with some activity.
If you rupture an Achilles tendon, you may feel a sharp, sudden pain. Most people report feeling or hearing a pop at the same time. You might see swelling and bruising and may not be able to point your foot down or stand on your toes.
If your Achilles tendonitis symptoms lead you to believe that you have ruptured your Achilles tendon, it is always a good idea to check with a qualified health care provider.
You can assist your doctor in diagnosing your Achilles tendonitis symptoms by being able to provide the answers to the following questions:
- How much pain do you have and does it lessen with rest?
- How did your injury happen?
- Did the pain begin suddenly or gradually?
- Are Achilles tendonitis symptoms worse after certain activities or at certain times of the day?
- Have you experienced other injuries in the ankle area?
- What kind of physical activities do you participate in?
- What types of shoes are you wearing during exercise or sporting activities?
The doctor will probably also ask questions about your past health history, what kind of medications you have been taking for the pain and examine the back of your leg for pain and swelling. If your Achilles tendonitis symptoms are severe or do not improve with initial treatment, your doctor may want you to get an X-ray, ultrasound scan or MRI to rule o more serious conditions.
Achilles Tendonitis is typically graded according to how severe it is:
- Mild - This level of tendon injury is characterized as pain in the Achilles tendon during or shortly after a particular physical activity like running.
- Moderate - With this level of Achilles tendonitis, the Achilles tendon may swell due to inflammation. In some cases, a hard lump may form in the tendon.
- Severe - For people who suffer from severe Achilles tendonitis, any weight bearing activity causes Achilles tendon pain. Occasionally, the Achilles tendon may rupture. When, Achilles tendon ruptures, it sometimes feels like a hard whack on the heel.
Who is prone to Achilles tendonitis?
Achilles tendonitis can happen to anyone but tends to occur most commonly in middle-aged men. People who have naturally flat feet, who are obese and who have tight calf muscles are also at increased risk for developing Achilles tendonitis symptoms because all three of these factors increase the strain on the Achilles tendon. Other health factors which increase the possibility of developing Achilles tendonitis are diabetes and high blood pressure.
Athletes who run in worn out shoes with little or no support increase their risk of developing Achilles tendonitis symptoms. Tendon pain also tends to occur more frequently in co weather than in warm weather, and if you run on hilly terrain, you are more likely to hurt your Achilles tendon than if you run on flat surfaces.
Do you suffer from Achilles Tendonitis symptoms?
If so, Click Here to learn more about Achilles Tendonitis treatment and prevention.
RELATED PRODUCTS:
OTHER RELATED TOPICS:
RUNNER OVERCOMES PRE-RACE ACHILLES TENDONITIS
MEDI-DYNE EARNS MAYO CLINIC PRODUCT ENDORSEMENTS
5 BEST HEEL CUPS FOR PLANTAR FASCIITIS
PLANTAR FASCIITIS, A REASON TO WORRY?
PLEASE NOTE: The information on this website and article is for information only and should not be used as a substitute for consulting your doctor. Consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and rehabilitation.